Advanced setup options for older modems
The Advanced Setup area of your modem's user interface lets you change several settings that give you greater control over your modem's operation. These settings are best for tech-savvy folks who understand a bit more than the typical user about modems and networking.
You can access the Advanced Setup menu by following the steps below:
1. Connect a device, such as a computer or tablet, to the internet through WiFi or using an Ethernet cable connected to your modem.
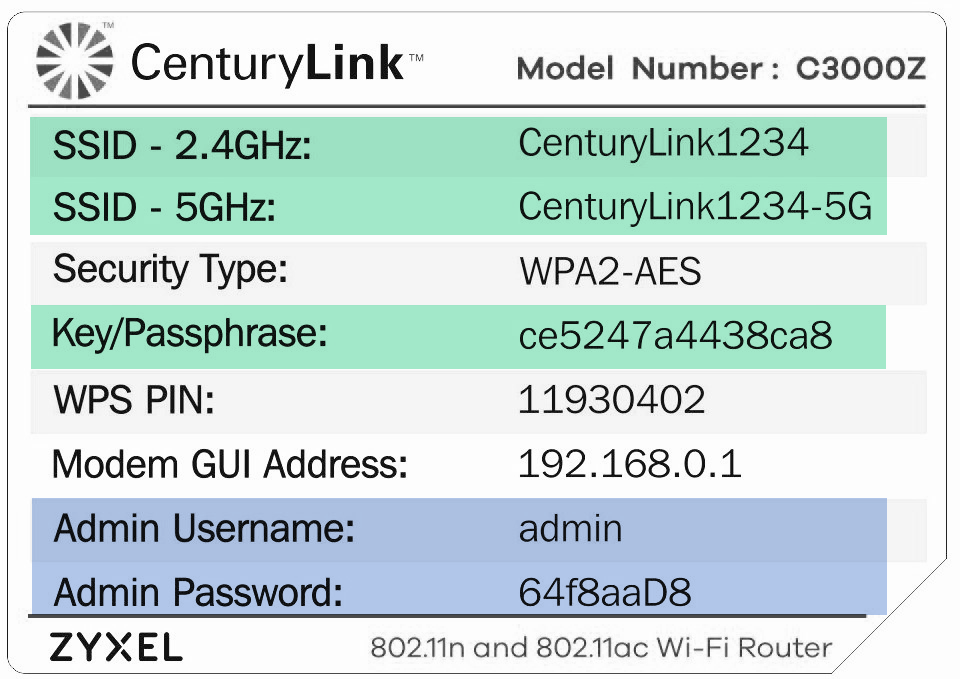
2. Open a web browser and type http://192.168.0.1 into the web address field.

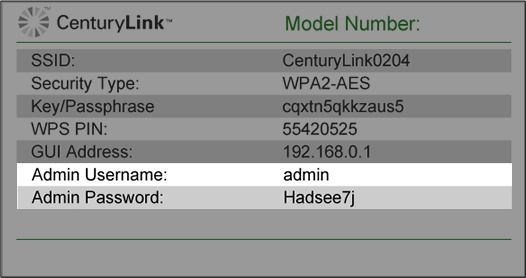
3. Log in to the modem's settings interface (Modem GUI) using your Admin Username and Admin Password. Unless you previously changed this information, you can find it on the modem label. Note that these are different from your wireless network name (SSID) and WiFi password (security key).
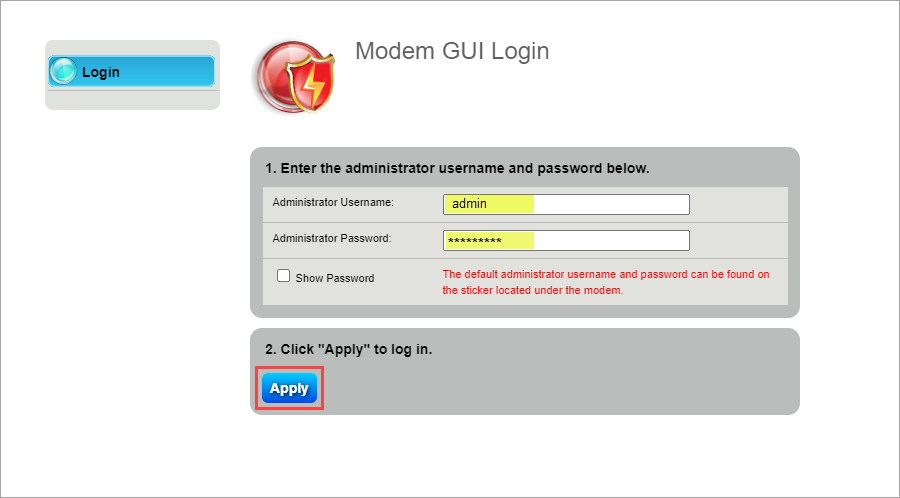
4. Select the Advanced Setup icon in the main menu.
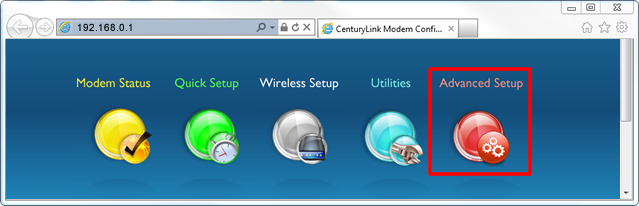
Then, you can select one of the options below to see additional step-by-step instructions on how to change each setting.
Blocking/Filtering
- Access Scheduler: Allows you to select a device connected to your network and set Internet access rules.
- Service Blocking: Allows you to select a device connected to your network and block specific Internet services.
- Website Blocking: Allows you to select a device connected to your network and block that device from accessing certain websites.
Broadband Settings: Allows you to change the connection parameters to your service provider. These settings should not be changed unless instructed by your ISP.
IP Addressing
- DHCP Settings: Allows you to edit the DHCP settings that define the LAN addressing parameters for your modem to allocate IP addresses to LAN devices.
- DHCP Reservations: Leases a permanent DHCP allocated address to a client.
- DNS Host Mapping: Creates a static hostname for the specified IP address in the DSL router. WAN and LAN IP addresses are supported.
- WAN Settings: Allows you to change the protocol and addressing type required by your ISP for Internet access. These settings should not be changed unless instructed by your ISP.
- Turn on IPv6: IPv6 is an upgrade of IPv4, the protocol that the internet runs on.
- Dynamic DNS: Associates the WAN IP address of your router with a hostname.
QoS: Prioritizes traffic types (such as VoIP) before standard data traffic. Traffic shaping your network with QoS can increase application performance and prevent your network from becoming overloaded.
Remote Management
- Remote GUI: Enables access to the router from a WAN connection. To access your modem remotely you will need to use https:// followed by the modem WAN IP address. You can manage the Administrator Username and Password for the modem GUI here.
- Remote Console: Enables telnet or SSH access to the router from a WAN connection using the WAN IP address of the modem.
Routing
- Dynamic Routing: Used if a gateway is set up behind the modem.
- Static Routing: Adds routers manually to the routing table. If a change or a failure occurs between two statically defined nodes, traffic will not be rerouted and must wait for the failure to be resolved by the administrator.
Security
- Administrator Password: Prevents outsiders from accessing the firmware settings of the modem. After creating a username and password, you will need to enter them every time you access the modem firmware GUI located at http://192.168.0.1.
- Application Forwarding: Forwards ports to the selected LAN device by application name.
- Port Forwarding: Allows you to enter ports or port ranges to forward Internet applications to a LAN device.
- DMZ Hosting: Enables a LAN device to use the modem WAN IP address as its own. DMZ places the LAN device outside the firewall.
- IPv4 Firewall: Activating the firewall is optional. When the firewall is activated, security is enhanced, but some network functionality will be lost.
- IPv6 Firewall: Activating the firewall is optional. When the firewall is activated, security is enhanced, but some network functionality will be lost.
- NAT (Network address translation): Turning off NAT will open your Broadband Modem to outside intrusion, creating a security risk. These settings should not be changed unless instructed by your ISP.
- UPnP: Simplifies the connection and implementation of devices to your network.
- SIP ALG: Enables or disables the ability to pass SIP sessions to the LAN.
Top modem/router topics
- Set up your modem and activate internet
- Connect devices to your WiFi network
- Should you use 2.4 or 5 GHz WiFi?
- Brightspeed compatible modems
- How to read your modem lights
- When and how to use modem reset
- How to return a modem
- How to upgrade your modem's firmware
- Modem or router: What's the difference?
View all Modem/Router topics
Top tools
Log in to access our most popular tools.
Was this page helpful?
Brightspeed services support

.png)




.png)